Ihlet Lifewater Concept Global Water Pollution Monitoring Network
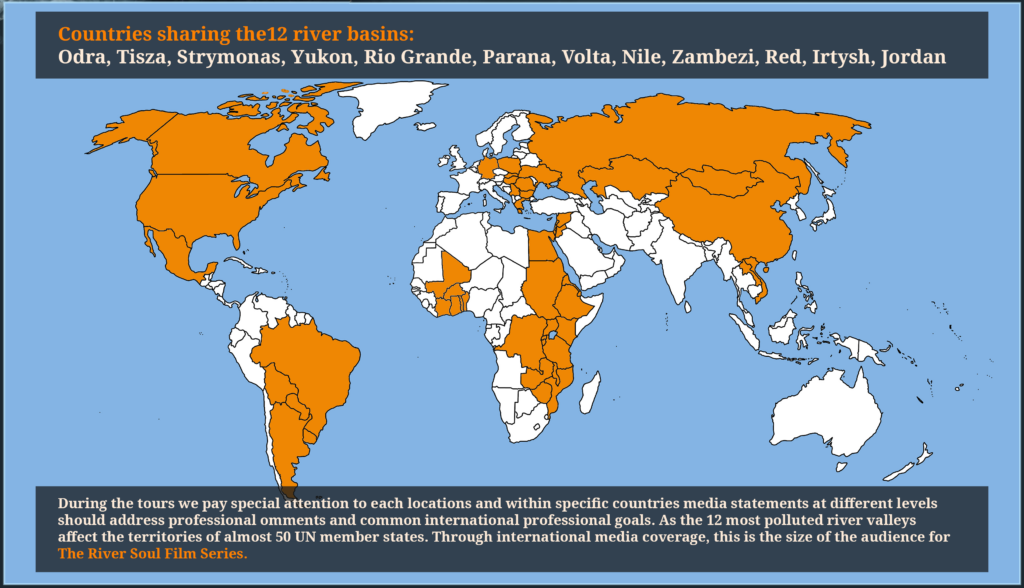
Why is Water Pollution Monitoring important?
Let’s see what the data shows us


Water pollution has never been a bigger problem
Plastics and other pharmaceuticals
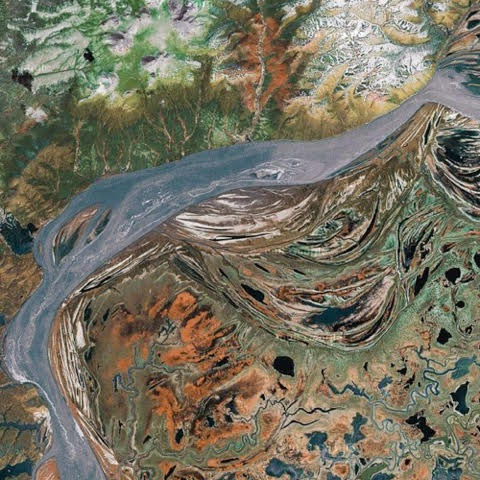
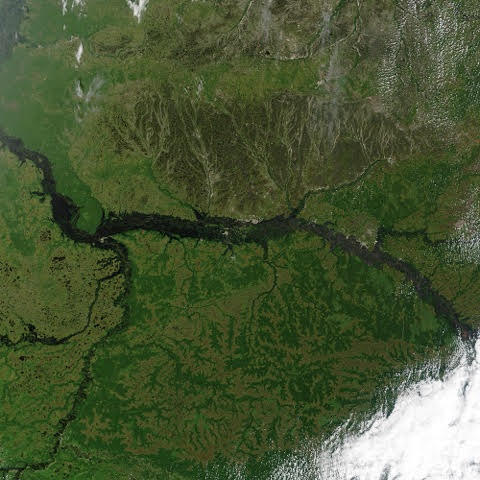



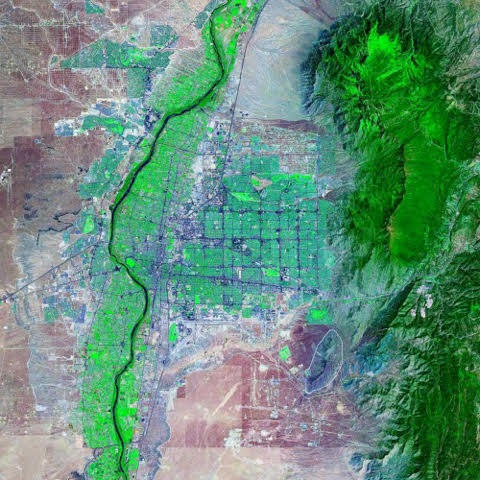
Yukon
854.700 km2
USA, Canada
Irtys
1.643.000 km2
Russia, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia
Rio Grande
472.000 km2
USA, Mexico
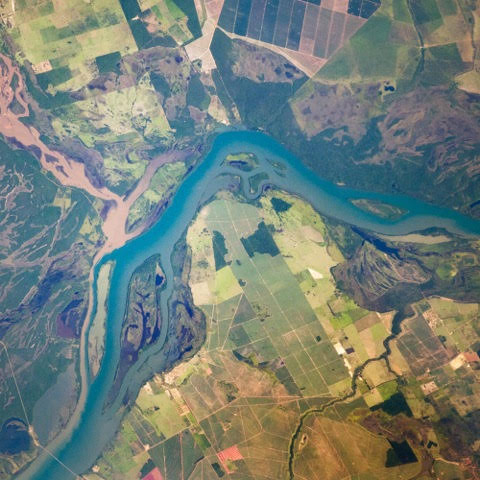



Parana
2.582.672 km2
Bolivia, Paraguay, Brasil, Uruguay, Argentina
Red River
143.700 km2
China, Laos, Vietnam
Nile
3.400.000 km2
Egypt, Sudan, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Uganda, Dem.Rep. Congo, Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi



Zambezi
1.390.000 km2
Zambia, Angola, Mozambik, Zimbabwe, Malawi, Namibia, Botswana
Odra
119.074 km2
Germany, Czech Republic, Poland
Jordan
41.650 km2
Jordan, Palestine, Israel, Syria, Lebanon, Egypt

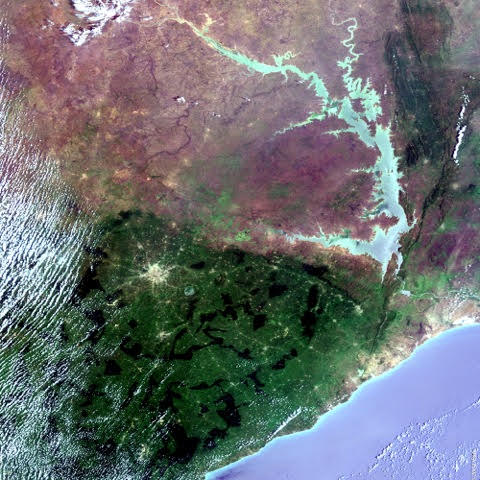

Strymonas 18,078 km² Bulgaria, Greece , Rep. of FYR Macedonia
Volta
407.093 km2
Ghana, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast, Mali, Togo, Benin
Tisza
157.000 km2
Slovakia, Serbia, Ukraine, Romania, Hungary
